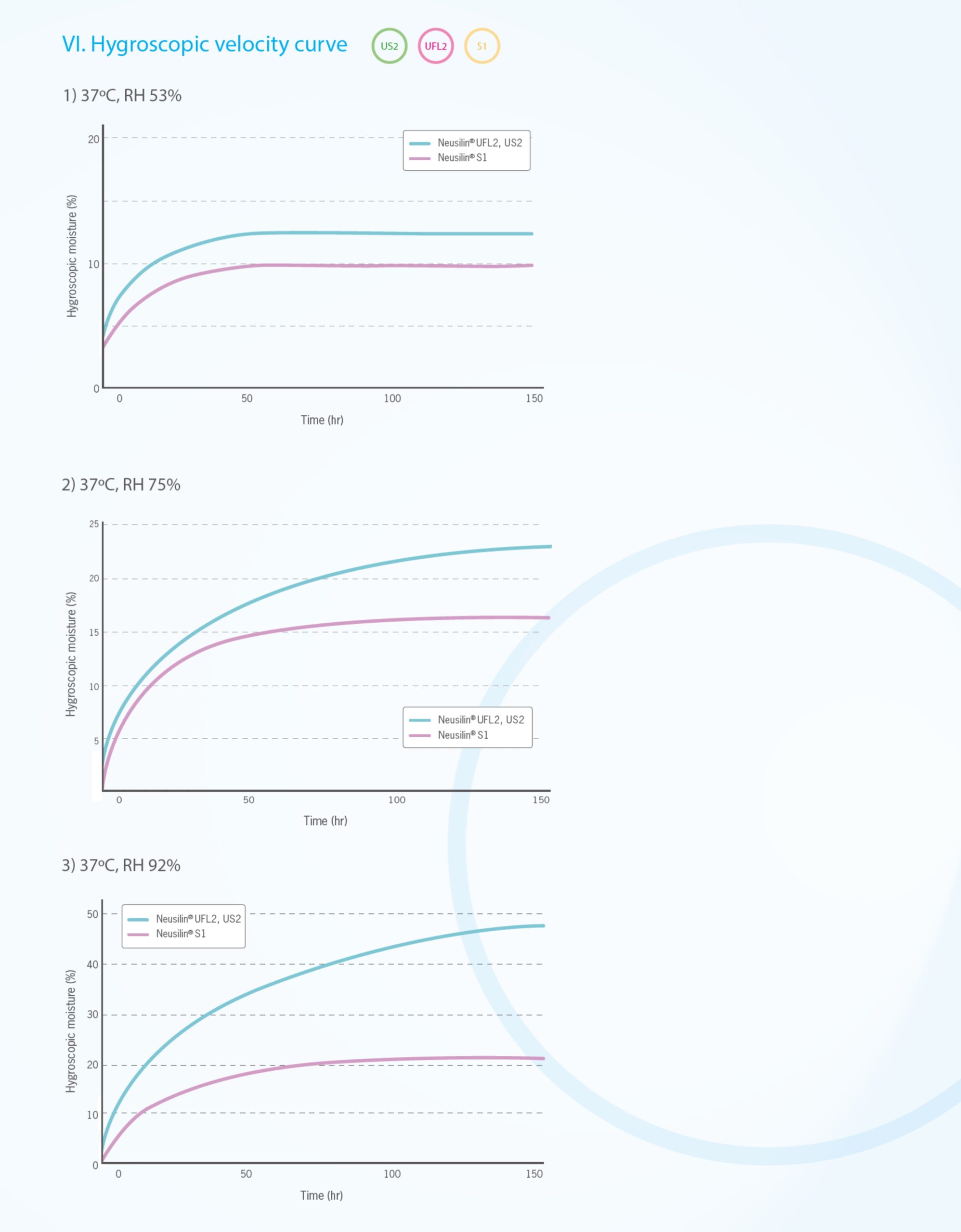
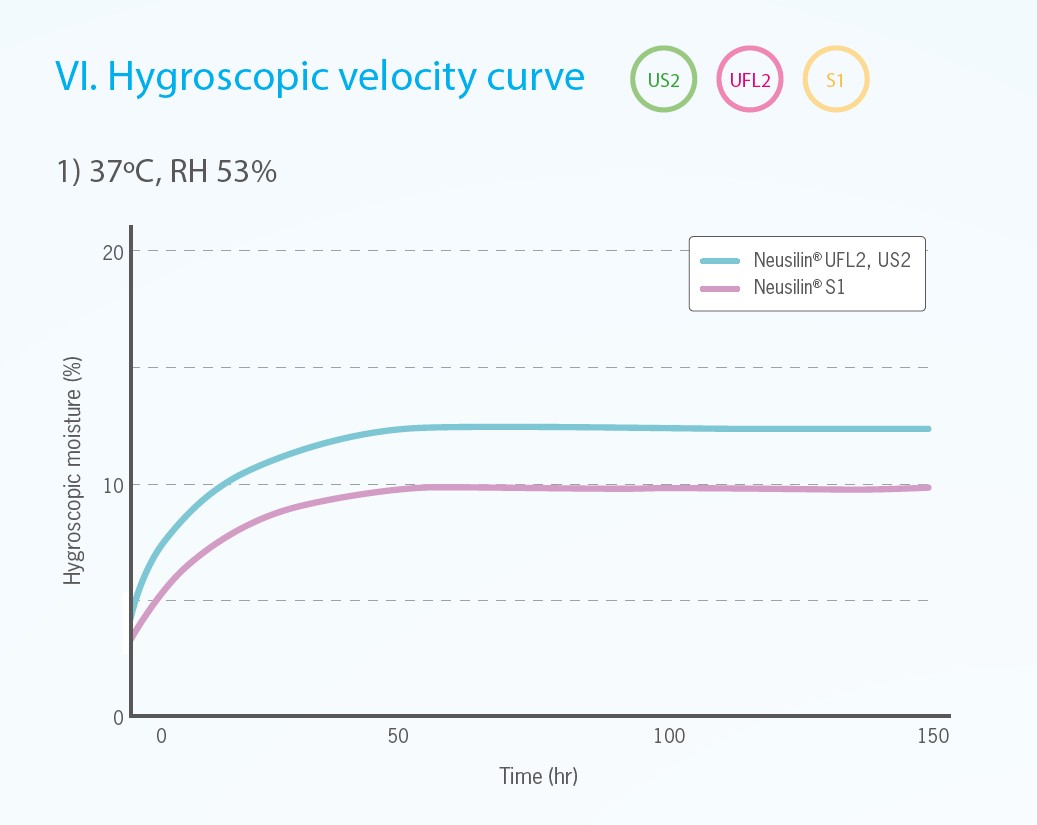
Neusilin® is available in various grades. The grades differ in bulk density, water content, particle, size and pH. The below contents describe the general properties and grades.
What is Neusilin®?
Neusilin® is a synthetic, amorphous form of magnesium aluminometasilicate that has a market present since 1954. First launched in Japan, and it was then marketed abroad.
Neusilin® solves common problems associated with tableting by facilitating consistent flow of powder mix, providing optimum tablet hardness at low compression forces, protecting the active ingredient from moisture related issues and converting oily or sticky APIs into free flowing powder.
General Properties of Neusilin®
Neusilin®
| Product Name | Neusilin® |
| Compendial name (JP, USP/NF & EP) |
Magnesium Aluminometasilicate |
| Composition (on dry basis)% |
Al₂O₃:29.1~35.5 MgO :11.4~14.0 SiO₂ :29.2~35.6 |
| Appearance | White powder or granules |
| Physical form | Amorphous |
| Solubility | Very slightly soluble in acids; practically insoluble or insoluble in water, in alcohol, and in alkalies |
| Thermal stability | Stable |
Neusilin® - The specialty excipient
Neusilin® is amorphous, possesses very large specific surface area and has high oil and water adsorption capacity. It is also highly-compressible. Neusilin® is widely used for improvement of the quality of tablets, powder, granules and capsules. The below are some of the application of Neusilin®
Exceptional Excipient Properties
Neusilin® has numerous applications as an excipient
- Flow Enhancement:
Neusilin® has high-surface area and disperse easily. It stick to the surface of other particles to aid flow.
- Anti-caking:
Neusilin® prevents caking at high humidity conditions for hygroscopic powders.
- Compressibility and Disintegration:
Neusilin® is superior in compressibility which enables to make hard tablets at low compression force. It can also maintain the tablet hardness in high-humidity. It can amplify the capillary forces that improves the disintegration of tablets.
- Powderization of oily actives:
High oil adsorption capacity enables powderization and tableting of oily actives:
Neusilin® grades
Please below for the list of grades available. PDF and image file (png) are also available for print-out.
Electron micrographs
UFL2
US2
S1
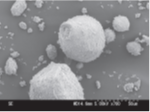
S2
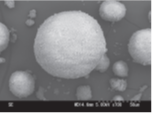
Typical properties
| GRADE | Alkaline | Neutral | |||||||
| S1 | S2 | UFL2 | US2 | ||||||
| Appearance | White granule | White granule | White powder | White granule | |||||
| Degree of whiteness (%) | > 95 | > 95 | > 95 | > 95 | |||||
| Loss on drying (%) 110°C, 7 hours | 13 - 20 | < 5 | < 7 | < 7 | |||||
| Bulk density | Loose (g/ml) | 0.30 - 0.37 | 0.29 - 0.37 | 0.06 - 0.11 | 0.13 - 0.18 | ||||
| Tapped (g/ml) | 0.36 - 0.43 | 0.34 - 0.42 | 0.10 - 0.17 | 0.16 - 0.22 | |||||
| True specific gravity | 2.0 | 2.2 | 2.2 | 2.2 | |||||
| Specific surface area (m2/g)*1 | 110 | 110 | 300 | 300 | |||||
| Average particle size (μm) | 112 | 115 | 3.1 | 106 | |||||
| Angle of repose (°) | 30 | 30 | 45 | 30 | |||||
| Oil adsorbing capacity (ml/g)*2 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 2.7 - 3.4 | 2.7 - 3.4 | |||||
| Water adsorbing capacity (ml/g) | 1.0 | 1.2 | 2.4 - 3.1 | 2.4 - 3.1 | |||||
| Acid consuming capacity (ml/g)*3 | >=210 | >=210 | >=210 | >=210 | |||||
| pH (4% slurry)*4 | 8.5 - 10.0 | 8.5 - 10.0 | 6.0 - 8.0 | 6.0 - 8.0 | |||||
*1) BET surface area, nitrogen adsorption method
*2) Japanese Industrial Standard pigment test method (JIS K5101)
*3) Amount of 0.1N hydrochloric acid neutralized by 1g dried product (110°C. 7 hours)
*4) Weigh 2 g of sample, add water to make 50 ml. After stirring, allow to stand for 2 minutes, Measure pH using pH meter